這些題目都很基礎不鑽牛角尖,主要功用是維持一種「程式的手感」;一次就寫出 bug-free 的程式碼是很不容易的,需要一段時間練習。
網路上有很多 online judgment 網站,Accept 之後的成績表可以看一下,盡量會最快的方法,可以看一下討論區的討論,迴圈解、遞迴解、數學解、Botton-up approach、Top-down approach ... 有很多可讀性很高又很短的程式碼,很值得學習:)
一、linked list
1. Dummy node trick
第一個要介紹的是 dummy node trick,dummy node 是為了解決 linked-list 中刪除 head 不便的問題,是非常常見的一個 trick。例如像下面的範例:
Remove Linked List Elements
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
class Solution { public: ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) { ListNode* dummyNode = new ListNode(0); // dummy node trick dummyNode->next = head; ListNode* cur = dummyNode; while(cur->next!=NULL){ // Keeping prev node is a good way to implement delete operator. if(cur->next->val==val) cur->next = cur->next->next; else cur = cur->next; } return dummyNode->next; // Don't return head because of special case } };
2. Reverse Linked List
接下來將 linked list 前後反轉 (reverse) 的寫法,有助於提升對 linked-list 操作的熟練度。
Reverse Linked List
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { ListNode *pre=NULL, *cur=head, *temp=NULL; while(cur!=NULL){ temp = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } };
程式可以搭配圖片閱讀:

reverse linked list 美圖 (Chiu CC 製)
3. fast-slow pointer trick
fast-slow pointer trick 有以下功能:
- 沒有 cycle 時,可以尋找此 linked-list 中點
- 有 cycle 時,fast pointer 和 slow pointer 兩者重合。
Linked List Cycle II
https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head==NULL) return NULL; if(head->next==NULL) return NULL; ListNode *fast=head, *slow=head; // fast-slow pointer trick while(fast->next!=NULL && fast->next->next!=NULL){ fast = fast->next->next; slow = slow->next; if(fast==slow) return checkPos(head, fast); // fast-slow pointer 重合。 } return NULL; } ListNode* checkPos(ListNode* head, ListNode* fast){ while(head!=fast){ // 會面點到 cycle begin 和 head 到 cycle begin 距離相同。 head = head->next; fast = fast->next; } return fast; } };
二、Binary Tree
1. Invert Binary Tree
遞迴暖身題,這題因為 homebrew 作者 Max Howell 的吐槽紅了一陣子,答案用簡單的遞迴就可以完成:)
Google: 90% of our engineers use the software you wrote (Homebrew), but you can't invert a binary tree on a whiteboard so fuck off.
原推文連結
class Solution { public: TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return root; TreeNode* temp = root->left; root->left = root->right; root->right = temp; invertTree(root->left); invertTree(root->right); return root; } };
2. Balanced binary tree validation
給定一個 binary tree,判斷該 tree 是否為 height-balanced (The depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.)。
Leetcode OJ - Balanced Binary Treehttps://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
1. Top-down Recursion Approach
直接把 Balanced Binary Tree 的數學定義寫成程式碼,非常直覺。但是 maxDepth() 會一直重複呼叫導致有重複計算的部分。
Time Complexity : $O(n^2)$
Space Complexity : $O(n)$
class Solution { public: bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { if(root==NULL) return 1; else return abs(maxDepth(root->left)-maxDepth(root->right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); } int maxDepth(TreeNode* root){ if(root==NULL) return 0; else return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1; } };
2. Bottom-up Recursion Approach
bottom-up 程式碼的順序很重要,當左子樹不平衡時,沒有必要再對右子樹求深度,要馬上 return -1,不可把兩個判斷式寫在一起。
通常一個問題 Top-down 比較容易想像且好解出答案,但是較迂迴的 Bottom-up 想法在複雜度上通常較有優勢;所以看到一個題目用直覺的 Top-down 解出答案後,一定要嘗試看看 Bottom-up 能不能構造出更精巧的演算法:D
Time Complexity : $O(n)$
Space Complexity : $O(n)$
class Solution { public: bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { if( maxDepth(root)==-1 ) return 0; else return 1; } int maxDepth(TreeNode* root){ if(root==NULL) return 0; int leftDepth = maxDepth(root->left); if(leftDepth == -1) return -1; int rightDepth = maxDepth(root->right); if(rightDepth == -1) return -1; if(abs(leftDepth-rightDepth) <= 1) return max(leftDepth, rightDepth)+1; else return -1; } };
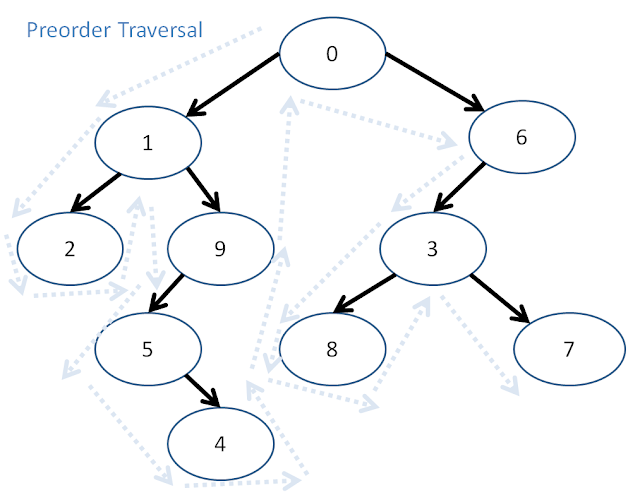
3. Binary tree inorder traversal
這題非常經典,recursion 和 iteration 是很基礎的 traversal binary tree 方法;而 Morris traversal 則是用到了 thread binary tree 的結構。
Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/description/
1. Recursive Approach
最直觀的方法,preorder、inorder 和 postorder 遞迴解。
class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderList, temp; vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { if(!root) return temp; inorderTraversal(root->left); inorderList.push_back(root->val); inorderTraversal(root->right); return inorderList; } };
2. Iterating method using Stack
用 iteration 解時通常會使用一個 stack,也是很基礎的寫法。 (其實 recursion 執行時也使用了 memory stack。)
class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { vector<int> inorderList; vector<TreeNode*> stack; TreeNode* curNode = root; while( curNode || !stack.empty() ){ if(curNode){ stack.push_back(curNode); curNode = curNode->left; } else{ TreeNode* popNode = stack.back(); stack.pop_back(); inorderList.push_back(popNode->val); curNode = popNode->right; } } return inorderList; } };
3. Morris traversal using thread binary tree
這個方法比較特別,用到了葉節點的 null pointer,可以實現 iteration 版本空間複雜度 O(1) 的 traversal。
class Solution { public: vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* curNode = root; vector<int> nodeList; while(curNode){ if (!curNode->left){ nodeList.push_back(curNode->val); curNode = curNode->right; } else{ TreeNode* pred = curNode->left; while (pred->right && pred->right!=curNode) pred = pred->right; if(!pred->right){ pred->right = curNode; curNode = curNode->left; } else { pred->right = NULL; nodeList.push_back(curNode->val); curNode = curNode->right; } } } return nodeList; } };
小結
大多的題目都能用這些 trick 變化一下解開,如 Palindrome Linked List,解法如下:
- 快慢指針找中點
- in-place 的 inverse link-list 方法
- 比較前後半 list 是否相同
另外還有一些細節,如 DP table 掃 index 的方式、動態陣列 ... 等等不勝枚舉,臨場遇到就要靠清楚的頭腦了:)
References
Chiu CC - Linked List: 新增資料、刪除資料、反轉
http://alrightchiu.github.io/SecondRound/linked-list-xin-zeng-zi-liao-shan-chu-zi-liao-fan-zhuan.html
soulmachine - Leetcode 題解
https://github.com/soulmachine/leetcode
siddontang - Leetcode 題解
https://siddontang.gitbooks.io/leetcode-solution/content/